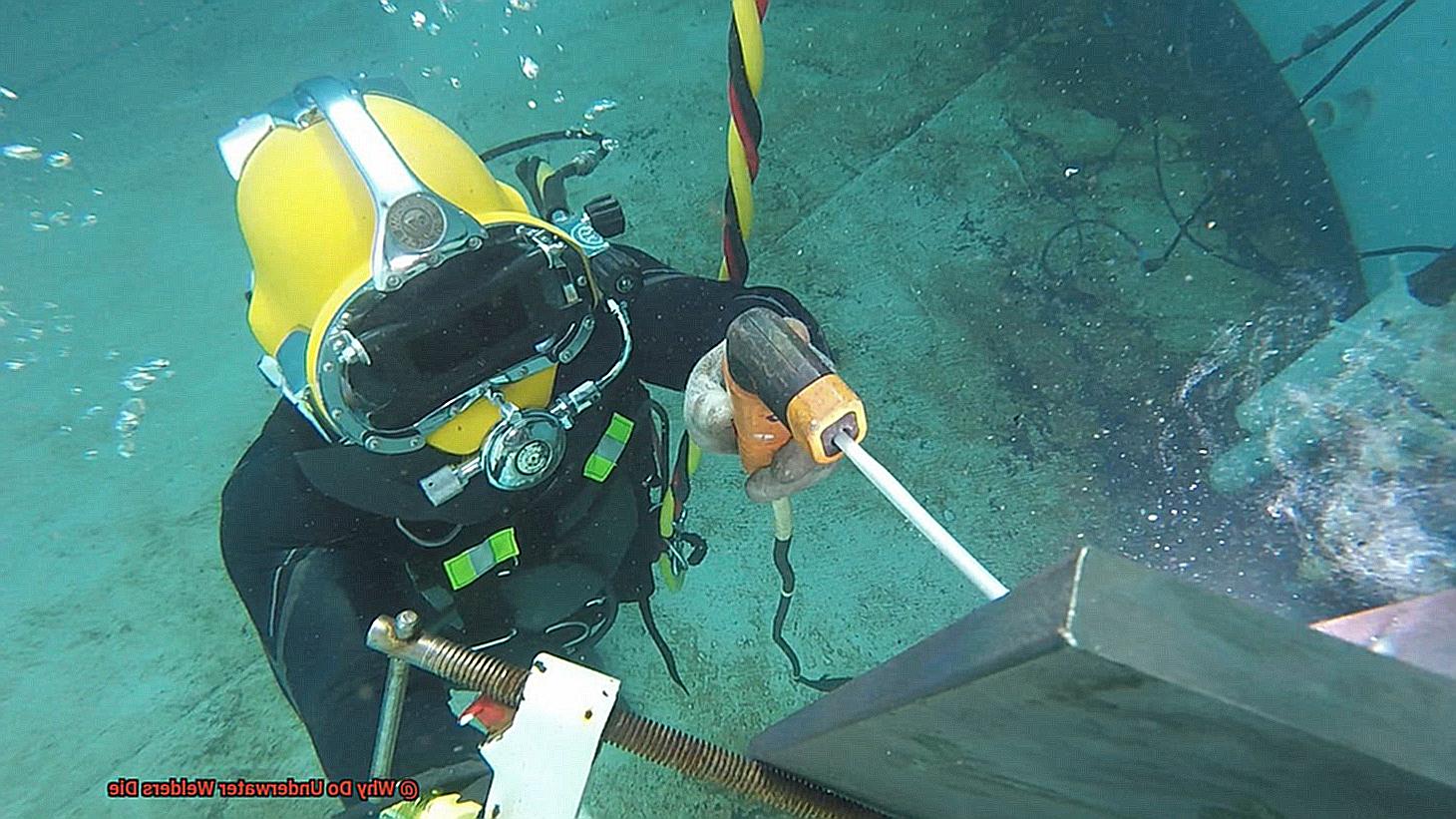
Have you ever stopped to consider why underwater welding is considered one of the most treacherous jobs in the welding industry? It’s not just because of the obvious risks that come with working underwater, such as drowning. In fact, the primary cause of fatalities in this profession is something entirely different.
So, what exactly makes underwater welding so hazardous? The answer lies in a deadly combination of two factors: electricity and water. When welders carry out their duties underwater, there’s a high risk of electric shock due to water’s conductivity. This can lead to severe burns or even cardiac arrest. But that’s not all; welding produces a significant amount of hydrogen gas, which can combine with oxygen in the water and cause explosions.
In addition to these risks, underwater welders face a range of other hazards like low visibility, strong currents, and frigid temperatures. To work safely and effectively in this challenging environment, welders need specialized equipment and extensive training.
In this blog post, we’ll explore the key factors that contribute to fatal accidents in underwater welding. We’ll delve into the unique challenges faced by welders who work beneath the waves and discuss precautions that can be taken to minimize risks. So let’s take a deep dive into this dangerous yet fascinating profession.
What is Underwater Welding?
Contents
Underwater welding is a fascinating and exhilarating job that requires a unique set of skills. This specialized process involves welding or cutting metal in a submerged environment, which presents many challenges for even the most experienced divers. So, what exactly is underwater welding, and why is it so exciting?
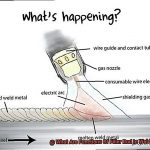
There are two main types of underwater welding: wet welding and dry welding. Wet welding is the most common method and involves the welder working directly underwater while wearing diving gear and using an electrode holder to create an arc between the welder and the metal being welded. On the other hand, dry welding creates a dry environment around the welding area using a chamber or habitat. The welder works inside the chamber wearing a dry suit and breathes air from a surface supply.
Underwater welders face several risks that can lead to injury or death. One of the main dangers is exposure to high-pressure environments, which can cause nitrogen narcosis and decompression sickness. In addition, electrical shock is a significant risk due to the high-voltage electricity used in welding, and working in saltwater increases the risk of electrocution. Finally, due to their heavy gear and equipment, underwater welders are also at risk of drowning.
Despite these risks, underwater welding plays a crucial role in maintaining offshore oil rigs, ships, and underwater pipelines. It requires specialized training, equipment, and safety protocols to minimize risks and ensure worker safety.
The Dangers of Underwater Welding
Underwater welding is a remarkable profession that demands welders to work in some of the most challenging environments. However, it’s also one of the most dangerous professions due to the countless risks that welders face. In this article, we will delve into the dangers associated with underwater welding.
Electrocution is one of the most significant hazards of underwater welding. Welders work with electricity, and when combined with water, it can be lethal. The presence of salt in seawater increases its conductivity, making it easier for electricity to flow through it. Welders must take extreme precautions when working near metal structures or pipelines to avoid electrocution. One small mistake could lead to a fatal shock.
Drowning is another significant danger that underwater welders face. They must wear bulky diving gear and work with heavy equipment while submerged in water, making it challenging to swim to safety if something goes wrong. Welders can also become entangled in cables and hoses, further increasing the risk of drowning. It’s essential for welders to remain calm and focused while working underwater, as panic can be deadly.
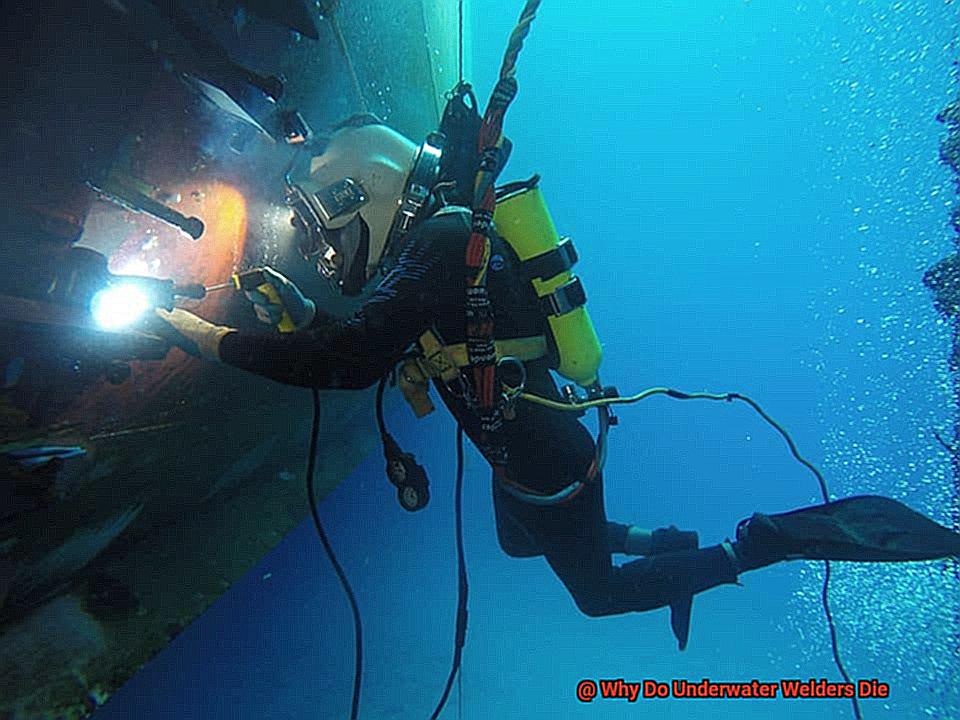

Decompression sickness is a severe condition that can occur when divers rapidly ascend to the surface after working at great depths for extended periods. This condition occurs when nitrogen bubbles form in the body tissues and bloodstream due to changes in pressure. If not treated quickly, decompression sickness can be fatal. Welders must follow strict decompression protocols to avoid this condition.
Explosions are also a significant risk associated with underwater welding. Welders must work in environments where there may be flammable gases or liquids present, which can ignite and cause an explosion. Additionally, the heat generated by welding can cause metal structures to expand and contract rapidly, leading to structural failure and potential explosions. One small spark could cause a catastrophic disaster.
To minimize these risks, strict safety protocols and procedures must be followed at all times. Underwater welders receive extensive training to ensure they are aware of the dangers associated with their job and know how to avoid them. They also use appropriate equipment such as protective clothing, helmets, and breathing apparatuses. Safety should always be the top priority while working underwater.
High Pressure Environments
The world of underwater welding demands immense courage, skill, and caution due to the many hazards involved, and one major risk factor is the high-pressure environment in which welders operate.
As soon as a welder submerges, they are exposed to much greater pressures than they would be on land. At just 33 feet deep, water pressure is already twice as high as it is on the surface. This intense pressure can trigger decompression sickness, also known as “the bends,” if a diver goes too deep or stays down for too long. This condition arises when nitrogen bubbles form in the bloodstream due to the sudden change in pressure. Symptoms can range from joint pain and fatigue to dizziness, paralysis, or even death.
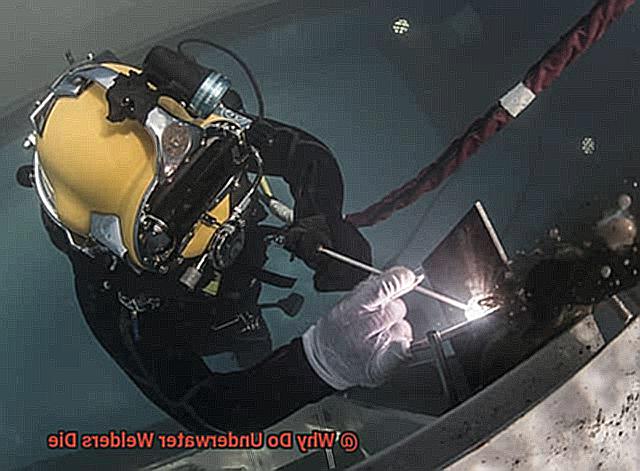

To prevent decompression sickness, underwater welders must adhere to strict diving protocols and use specialized equipment such as decompression chambers. However, accidents can still happen, and even the smallest error can be fatal. High-pressure environments can also cause other health issues such as ear barotrauma and sinus squeeze.
It is crucial for underwater welders to undergo rigorous training and follow safety protocols to ensure their well-being in high-pressure environments. However, even with proper precautions, the risk of injury or death cannot be entirely eliminated.
Electrical Shock Risks
While there are many hazards that underwater welders can encounter, one of the most severe and life-threatening risks is electrical shock.
Electrical shock occurs when a welder comes into contact with an electrically charged object or conductor. Since underwater welders work in a conductive medium, they are more prone to electrical shocks than those who work on land.
There are several factors that contribute to electrical shock risks in underwater welding. First and foremost, poor insulation of welding equipment is a significant source of danger. If the insulation is damaged or worn out, electricity can leak into the water and create an electric field around the welding site. Any welder who comes into contact with this field can experience muscle contractions, burns, and even cardiac arrest.
Improper welding techniques can also increase the chances of electrical shock. Welders must be trained to use proper grounding techniques, such as ensuring that all welding equipment is correctly grounded before starting work. Failing to do so can create stray currents that flow through the water and increase the risk of electrical shock.
To prevent accidents and fatalities due to electrical shocks, it is crucial to follow proper safety procedures. Welders must wear protective gear, including rubber gloves and boots, to minimize the risk of electric shock. They should also avoid working near live electrical circuits or equipment.
Drowning Hazards
One of the most severe dangers that underwater welders face is drowning. In this article, I will explain the various drowning hazards associated with underwater welding and how to mitigate them.

Underwater welding can be a life-threatening job due to the risk of equipment malfunction, lack of proper training, and hazardous working conditions. Welders working underwater are entirely dependent on their equipment to stay alive, and any malfunction or damage can lead to drowning. The use of electrical currents during welding generates hydrogen gas that can form bubbles, reducing visibility and trapping a welder who may not be able to escape and can drown.
The environment in which underwater welders operate can also be hazardous. Strong currents, rough seas, and low visibility can make it difficult for a welder to work safely. Moreover, cables or debris in the water can entangle a welder, preventing them from surfacing for air.
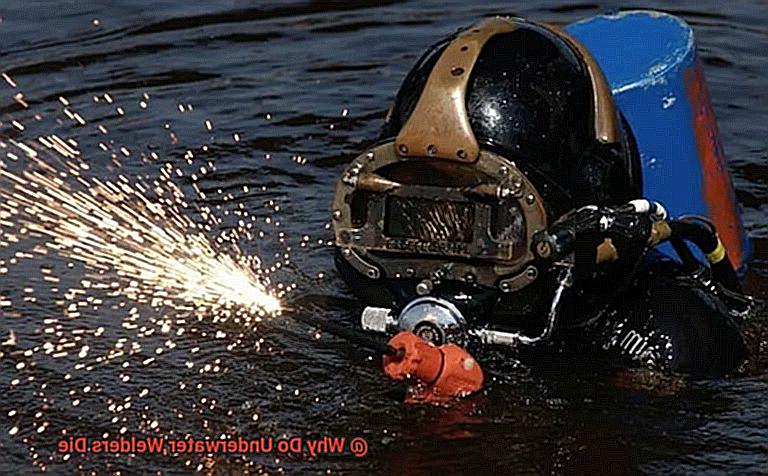

To mitigate the risk of drowning, comprehensive training on safety procedures and equipment usage is crucial for underwater welders. They should be aware of their surroundings before beginning work and always follow proper safety procedures. Employers must take responsibility for ensuring that all equipment is well-maintained and functioning properly before sending workers into the water, including having backup equipment available in case of failure.
In conclusion, drowning is one of the most significant risks associated with underwater welding. To stay safe on the job, underwater welders must wear protective gear, stay alert to their surroundings, and follow proper safety procedures. Employers must also provide adequate training and ensure all equipment is in good condition to avoid tragic accidents.
Safety Protocols for Underwater Welders
Underwater welding is an exciting and challenging profession, but it’s not without its risks. That’s why safety protocols are crucial for any underwater welding project. The safety of the welder should always be top priority, and it’s essential to ensure that all the necessary safety equipment is in place before starting any underwater welding task.
No underwater welder can work without the proper diving gear, such as a drysuit, helmet, and breathing apparatus. Personal protective equipment like gloves, boots, and eye protection are also necessary to ensure that the welders are well-protected. Additionally, specialized welding equipment designed explicitly for underwater use must be utilized to prevent electric shock by isolating the welding current from the surrounding water.
Electric shock is one of the most significant dangers of underwater welding. Underwater welders must be trained in proper electrical safety protocols to avoid any accidents. They must also regularly inspect their equipment for damage or malfunctions that could lead to electric shock. By doing so, they can prevent potentially fatal accidents.
Another major risk of underwater welding is decompression sickness or “the bends.” This occurs when a diver ascends too quickly from a deep dive, causing nitrogen bubbles to form in their bloodstream. To prevent this from happening, divers must follow strict decompression protocols after each dive. This involves slowly ascending to the surface while stopping at various depths to allow the body time to adjust to the pressure changes.
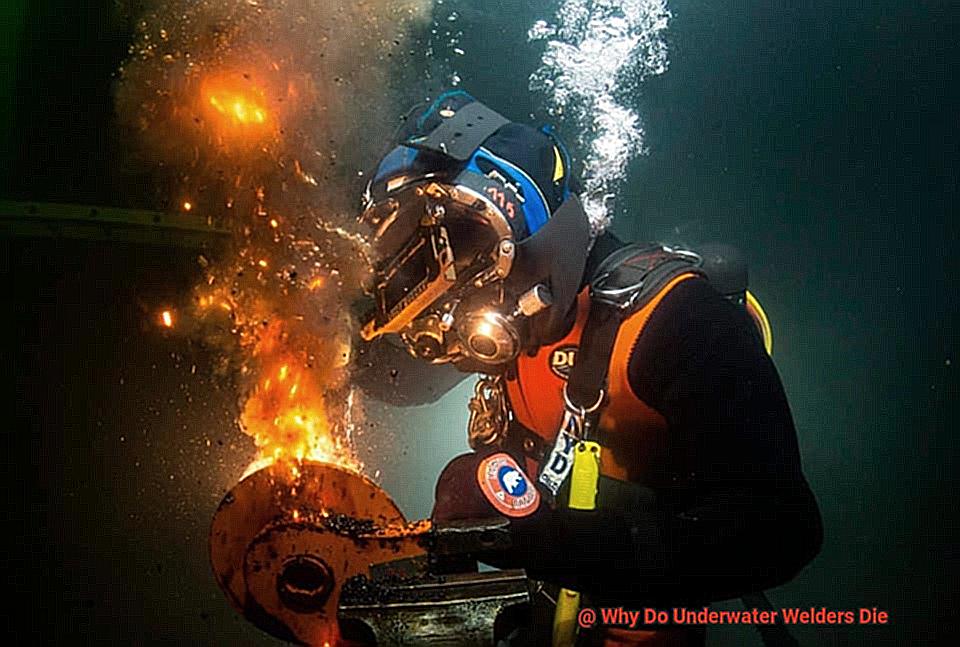

In addition to these safety measures, emergency protocols are also necessary for underwater welders. Knowing how to respond to equipment malfunctions, diving-related injuries, and other potential hazards can mean the difference between life and death in a dangerous situation.
Overall, safety protocols are crucial for the protection of underwater welders. By following these guidelines and using proper safety equipment, welders can minimize their risk of injury and ensure a successful project outcome. If you’re interested in pursuing a career in underwater welding, be sure to prioritize safety and undergo thorough training to protect yourself and those around you.
xvHWNH2w9h0″ >
Conclusion
Underwater welding is a captivating profession that demands skill, courage, and caution. However, it also poses significant risks that can lead to fatalities. The primary cause of these tragedies is the lethal combination of electricity and water. Due to water’s conductivity, welders face the risk of electric shock, which can result in severe burns or even cardiac arrest. Moreover, underwater welding produces hydrogen gas that can combine with oxygen in the water and cause explosions.
Apart from these hazards, underwater welders must contend with low visibility, strong currents, frigid temperatures, exposure to high-pressure environments, and drowning. To work safely and effectively in this challenging environment requires specialized equipment and extensive training.
Despite these dangers, underwater welders play an indispensable role in maintaining offshore oil rigs, ships, and underwater pipelines. However, they must take strict safety precautions to minimize risks and ensure their safety. This includes wearing protective gear such as drysuits, helmets, gloves, boots, eye protection and breathing apparatuses. Additionally, following proper electrical safety protocols during welding projects is crucial to avoid accidents.
Moreover, emergency protocols are necessary for underwater welders to respond quickly to equipment malfunctions or diving-related injuries. Safety should always be the top priority while working underwater.
In conclusion, while underwater welding offers exciting opportunities for skilled professionals seeking a unique challenge; it comes with significant dangers that require utmost attention. Welders must undergo rigorous training and follow strict safety protocols to minimize risks while working in high-pressure environments. By prioritizing safety measures such as personal protective equipment usage and following proper electrical safety protocols during welding projects can help prevent potentially fatal accidents from occurring.