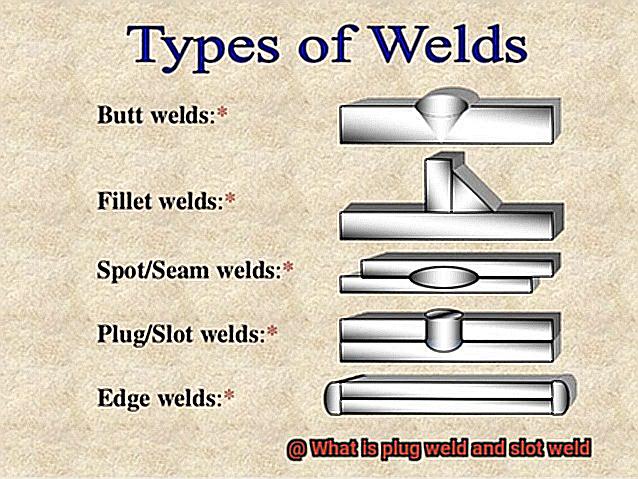
Do you ever find yourself marveling at the strength and durability of metal structures and wondering how they’re held together? The answer lies in the art of welding, a complex process that requires a specific set of skills and knowledge. Two popular techniques used in welding are plug weld and slot weld, which require precision, control, and expertise in thermal physics and metallurgy.
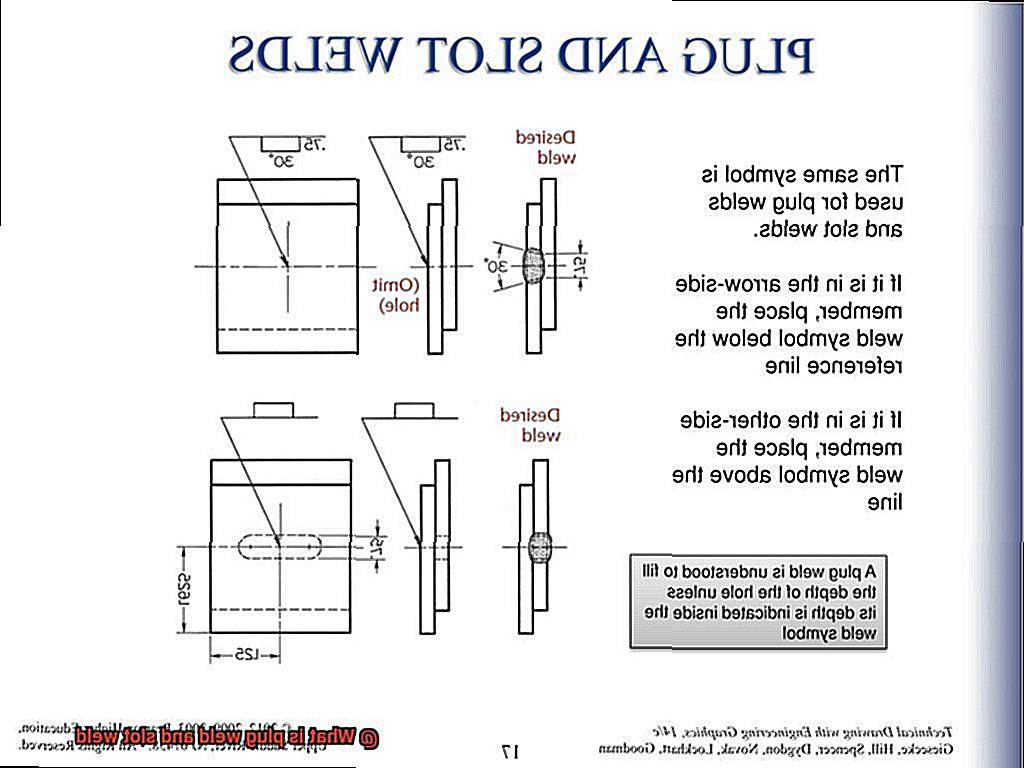
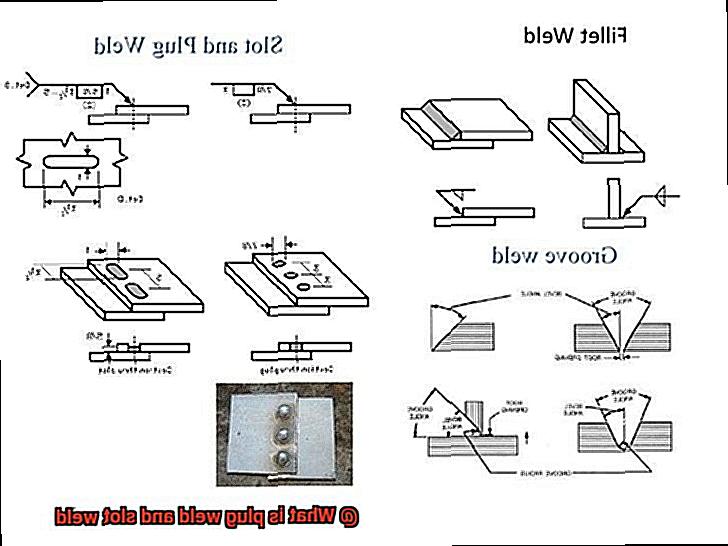
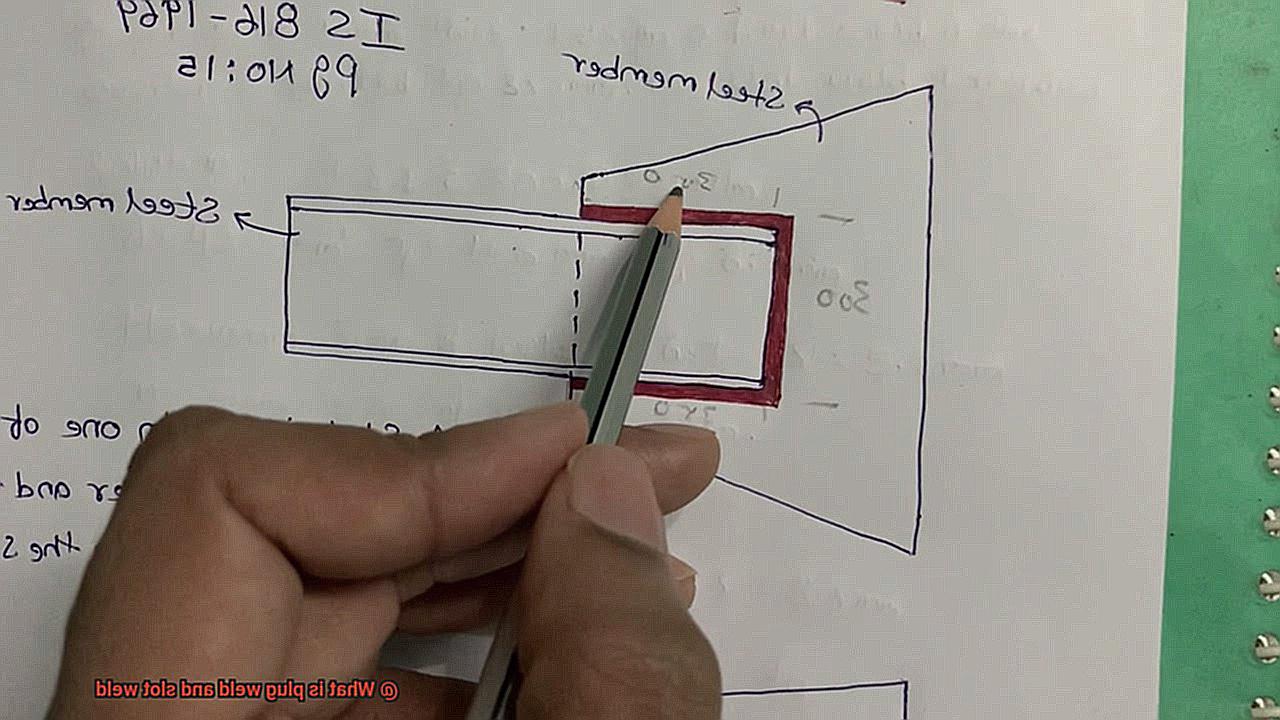
A plug weld is essentially the process of joining two pieces of metal by filling a hole with weld material. Meanwhile, a slot weld connects two metal plates by filling a slot cut into one or both plates. Although these techniques may seem straightforward, they require a high level of skill and understanding of welding principles.
Plug welds and slot welds are commonly used in various industrial applications such as automotive, construction, and manufacturing. In this blog post, we’ll take an in-depth look at these techniques to explore their principles, execution processes, advantages and disadvantages, as well as their significance in welding. By the end of this article, you’ll have gained an expert-level understanding of plug welds and slot welds. So let’s dive right into it.
What Are Plug Welds?
Contents
When it comes to welding, plug welds reign supreme as one of the most commonly used types of welding. So, what exactly are plug welds? Simply put, this welding method involves filling a hole or slot in one metal plate with molten metal from the other plate to create a sturdy and durable joint.
Plug welds offer several advantages over other types of welding. For starters, they require less preparation time, making them a popular choice in manufacturing industries where large quantities of welded components need to be produced quickly. Additionally, plug welds create a smooth and flush surface, which is ideal for automotive body panels or sheet metal fabrication.
However, it’s important to note that plug welds do have their limitations. They may not be suitable for joining materials that are significantly different in thickness or composition, or for applications where the joint will be exposed to extreme temperatures or corrosive environments. In such cases, other types of welding or joining methods may be more appropriate.
Despite these limitations, plug welds remain a versatile and effective method for joining metal components together. With proper preparation and execution, they can create strong and reliable joints that will last for years to come.
What Are Slot Welds?
Slot welding is a powerful and versatile welding technique that is widely used in construction and manufacturing. It involves cutting a slot in one piece of metal and welding it to another, resulting in a strong joint that can withstand the most demanding conditions.
The size and shape of the slot can vary depending on the thickness and type of metal being welded. Full slot welds involve welding along the entire length of the slot, while partial slot welds only involve welding along a portion of the slot. Additionally, there are various joint configurations to choose from, including T-joints, lap joints, and butt joints.
T-joints involve welding one piece of metal to the center of another piece of metal that is perpendicular to it. Lap joints overlap two pieces of metal and weld them together at the point where they overlap. Butt joints occur when two pieces of metal are placed end-to-end and welded together.
One of the primary benefits of slot welding is its ability to provide a strong joint between two pieces of metal. By welding along the entire length of the slot, both pieces are securely joined together. This makes slot welding particularly effective when used in applications that require high strength joints, such as heavy machinery or construction equipment.
Different Types of Welding Processes Used for Plug and Slot Welds
Each process has its unique strengths and weaknesses, making it essential to choose the right one based on factors such as material type, thickness, and budget.
Gas Tungsten Arc Welding
One popular method is Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), also known as TIG welding. This process is perfect for welding materials such as stainless steel, aluminum, and magnesium. It uses a tungsten electrode to create an arc that heats the metal, while a separate filler metal is added to create the weld. The result is a precise and clean weld with minimal spatter.
Gas Metal Arc Welding
Another common method is Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), or MIG welding. This process uses a wire electrode that is fed through a gun and melted by an electric arc to create the weld. It’s ideal for welding materials like steel and aluminum, providing a stable and consistent weld.
For thicker materials such as steel and iron, Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), also known as stick welding, is an excellent choice. It involves using a coated electrode that is melted to create the weld. This method allows for strong, deep penetration, making it suitable for heavy-duty applications.
Flux-Cored Arc Welding
Finally, Flux-Cored Arc Welding (FCAW) is similar to MIG welding but uses a hollow wire filled with flux instead of a solid wire electrode. The flux helps shield the weld from contaminants and creates a stronger bond between the base material and filler metal. This process is ideal for outdoor applications or when working with dirty or rusty materials.
With each of these welding processes having its set of advantages and disadvantages, it’s crucial to choose the right one for your specific needs. By selecting the appropriate method based on factors such as material thickness, cost, and time constraints, you can ensure that your welds are strong, durable, and long-lasting.
Advantages of Using Plug and Slot Welds
When it comes to welding techniques, there are various options available to welders, each with its unique strengths and weaknesses. However, among them, plug and slot welds offer several advantages that make them stand out from the rest.
One of the most significant advantages of using plug and slot welds is their ease of preparation and execution. Even novice welders can perform them with minimal training or specialized equipment. This makes them an accessible and affordable option for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts.
In addition to being accessible, plug and slot welds also offer superior strength and durability compared to other welding techniques. The material is fused together with the base metal, creating a bond that can handle heavy loads and stress. They can be used in a variety of materials, including steel, aluminum, and other metals.
Another significant advantage of using plug and slot welds is the smooth finish they create. Unlike other types of welding that leave scars or marks on the surface of the metal, plug and slot welds result in a clean finish that blends seamlessly with the surrounding material. This makes them an ideal choice for applications where appearance is essential, such as automotive or architectural projects.
Lastly, plug and slot welds are cost-effective in terms of both time and money. They require less preparation time and material than other welding techniques, making them an efficient option that saves both time and money in the long run.
Common Applications for Plug and Slot Welds
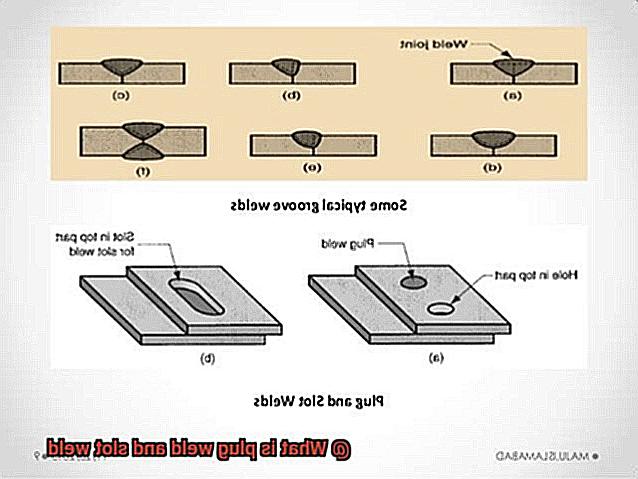
These versatile welding techniques offer a strong and efficient way to join metal sheets or plates together. They’re widely used in various industries, including automotive manufacturing, shipbuilding, and construction, due to their strength and accessibility.
In the automotive industry, plug welds are commonly used to join sheet metal parts together. Whether it’s creating body panels or brackets, plug welds offer a reliable and cost-effective solution. Slot welds are also used in the automotive industry to join structural components like suspension brackets and engine mounts.
In shipbuilding, plug welds are utilized to join plates or panels together for hull construction. They’re also frequently used in ship decks and bulkheads. Slot welds are similarly used in shipbuilding for joining structural members like frames and longitudinal beams, providing a secure and durable connection.
In construction, both plug and slot welds have various applications. Plug welds can be used for joining steel beams or columns together, providing a sturdy foundation. Whereas slot welds can be used for connecting steel plates or angles to a structural member, ensuring a seamless finish.
One of the key benefits of using plug and slot welds is that they offer unparalleled strength that blends seamlessly with the surrounding material. Additionally, they don’t require specialized equipment or extensive training, making them an accessible option for various welding projects.
Tips for Successful Plug and Slot Welding
There are several tips and techniques that can help ensure your welds are strong and reliable. In this blog post, we’ll dive into the importance of proper fit-up, electrode selection, welding technique, weld size, preheat, and post-weld treatment.
Proper fit-up is the foundation of a successful plug or slot weld. Before starting any welding job, make sure the surfaces that will be welded together are clean and free of any debris or contaminants. Proper alignment and a tight fit will help create a strong weld.
Choosing the right electrode is also crucial for creating a successful plug or slot weld. The electrode used should match the base metal being welded to ensure that the weld metal will have similar properties as the base metal.
Using the proper welding technique is equally important for creating strong welds. Maintaining a consistent arc length, keeping the wire at the appropriate angle, and using the right amount of heat are all essential for a successful weld. A steady hand and proper travel speed are also critical for creating a strong joint.
Weld size is another factor to consider when performing plug and slot welding. The size of the weld should be appropriate for the application. A weld that is too small may not provide sufficient strength, while a weld that is too large may cause distortion or weakening of the base metal.
Preheating the base metal before welding can help prevent cracking and ensure proper fusion of the weld metal with the base metal. Additionally, post-weld treatment may be necessary to prevent cracking or failure over time. This could include stress relieving, heat treatment, or other processes.
Finally, practice makes perfect. Take time to practice your plug and slot welding techniques on scrap material before tackling a larger project.
R8l6YIKFhbI” >
Conclusion
In conclusion, plug welds and slot welds are two popular welding techniques that require precision, control, and expertise in thermal physics and metallurgy. Plug welding involves filling a hole or slot in one metal plate with molten metal from the other plate to create a sturdy joint. On the other hand, slot welding involves cutting a slot in one piece of metal and welding it to another to create a strong joint that can withstand demanding conditions.
These versatile welding techniques offer several advantages over other types of welding. They are easy to prepare and execute, provide superior strength and durability, have a smooth finish, and are cost-effective. As such, they are widely used in various industries such as automotive manufacturing, shipbuilding, and construction.
To ensure successful plug and slot welding, proper fit-up, electrode selection, welding technique, weld size, preheat, and post-weld treatment are crucial factors to consider. Practice is also essential for developing the necessary skills to perform these techniques effectively.
Overall, plug welds and slot welds remain a reliable method for joining metal components together.