Welding is a crucial process that plays a vital role in various industries, including construction and manufacturing. However, porosity in welding can be a significant problem that can weaken the joint and render it ineffective. Porosity occurs when tiny holes or voids appear within the weld due to trapped gas in the molten metal. These gas pockets can cause cracks, corrosion, and even complete failure of the welded joint over time.
But fret not. With the right knowledge and skills, porosity can be prevented in welding. In this blog post, we will delve into everything you need to know about preventing porosity in welding. We will start by defining what porosity is and why it poses a challenge for welders. We will then explore the root causes of porosity, which include factors such as welding techniques, materials used, and environmental conditions.
Our focus will then shift towards discussing specific strategies for preventing porosity in your welding projects. From selecting the appropriate welding technique and materials to properly preparing metal surfaces, we will cover all essential steps for producing strong and solid welds without any porosity.
Whether you are an experienced welder looking to refine your skills or a novice just starting in the world of welding, this blog post has got you covered with valuable insights and practical tips for preventing porosity in welding. Get ready to up your welding game and produce flawless welded joinings every time.
What is Porosity in Welding?
Contents

Welding is a fundamental process used in various industries, ranging from construction to manufacturing. It involves the fusion of two or more metal parts using heat and pressure. However, welding can be challenging, and one of the most common issues welders encounter is porosity.
Porosity occurs when small voids, holes, or cavities form in the weld metal. These voids weaken the weld’s strength, reduce its durability, and make it more prone to corrosion and other forms of damage. Porosity also affects the weld’s appearance, making it less aesthetically pleasing.
Several factors can cause porosity in welding, including inadequate shielding gas, contaminated materials, poor surface preparation, and incorrect welding techniques. When the welding process doesn’t have proper shielding gas coverage, air can contaminate the weld pool, leading to porosity. Contaminated materials such as rusty or dirty metal can introduce impurities into the weld pool that cause porosity. Poor surface preparation can also prevent proper bonding between metals leading to porosity.
To prevent porosity in welding, it’s essential to follow proper welding procedures and use clean materials free from contaminants. Welders should maintain proper shielding gas throughout the welding process to prevent air from contaminating the weld pool. Correct welding techniques such as using appropriate travel speed, electrode angle, or arc length can ensure a strong and durable weld free from porosity.
Causes of Porosity in Welding

Welding is the art of combining two metal parts to form an unbreakable bond. However, as with any relationship, welding can encounter problems, and one of the most common issues is porosity. Porosity is a welding defect that can weaken the weld and compromise the structural integrity of the workpiece. The presence of gas pockets or voids in the weld metal causes this issue.
Several factors can contribute to porosity in welding. One of the primary causes is moisture or contaminants present on the surface of the workpiece or filler material. When these contaminants vaporize during the welding process, they create gas pockets in the weld metal. Therefore, it’s crucial to clean and prepare welding surfaces thoroughly before starting any welding operation.
Improper shielding gas coverage is another significant cause of porosity in welding. Shielding gas protects the weld from atmospheric gases that can cause contamination and porosity. However, if there isn’t enough shielding gas coverage or if there are leaks in the gas supply system, atmospheric gases can enter the weld and cause porosity.
Additionally, improper welding techniques or parameters can also contribute to porosity. A long or short arc length or fast or slow welding speed can affect arc stability and lead to porosity.
To prevent porosity in welding, it’s crucial to combine proper preparation techniques with careful attention to welding parameters and techniques. Welders must ensure adequate shielding gas coverage and use appropriate welding techniques for each application. By addressing these factors, welders can produce high-quality and durable welds that are free from defects like porosity.
Cleaning the Base Metal
Welding is an art form that requires precision, skill, and attention to detail. As a welder, you know that even the slightest mistake can compromise the strength and durability of your workpiece. That’s why cleaning the base metal is a critical step in ensuring that your welds are free from porosity.
Porosity occurs when gas pockets form during welding due to contamination or foreign material on the surface of the metal. To avoid this issue, it is essential to clean the base metal thoroughly before beginning the welding process.
Mechanical preparation is a highly effective method for cleaning the base metal. By using wire brushes, grinders, or sandpaper, you can remove rust, dirt, or oil from the surface of the metal. The goal is to create a smooth and clean surface that is free from any contaminants.
However, in some cases, stubborn contaminants may require chemical cleaning. This method involves using solvents or acids to dissolve grease or oil on the surface of the metal. It’s important to exercise caution when working with chemicals and follow all safety precautions.
Another critical factor in preventing porosity is keeping the welding surface dry. Moisture can cause gas pockets to form in the weld, leading to porosity. Therefore, it’s crucial to ensure that the base metal is dry and free from any moisture before starting the welding process.
Selecting the Appropriate Welding Technique and Parameters
As a skilled welder, you understand the importance of producing flawless welds. However, porosity can be a major issue that can compromise the strength and quality of your work. Fortunately, you can prevent porosity by selecting the appropriate welding technique and parameters.
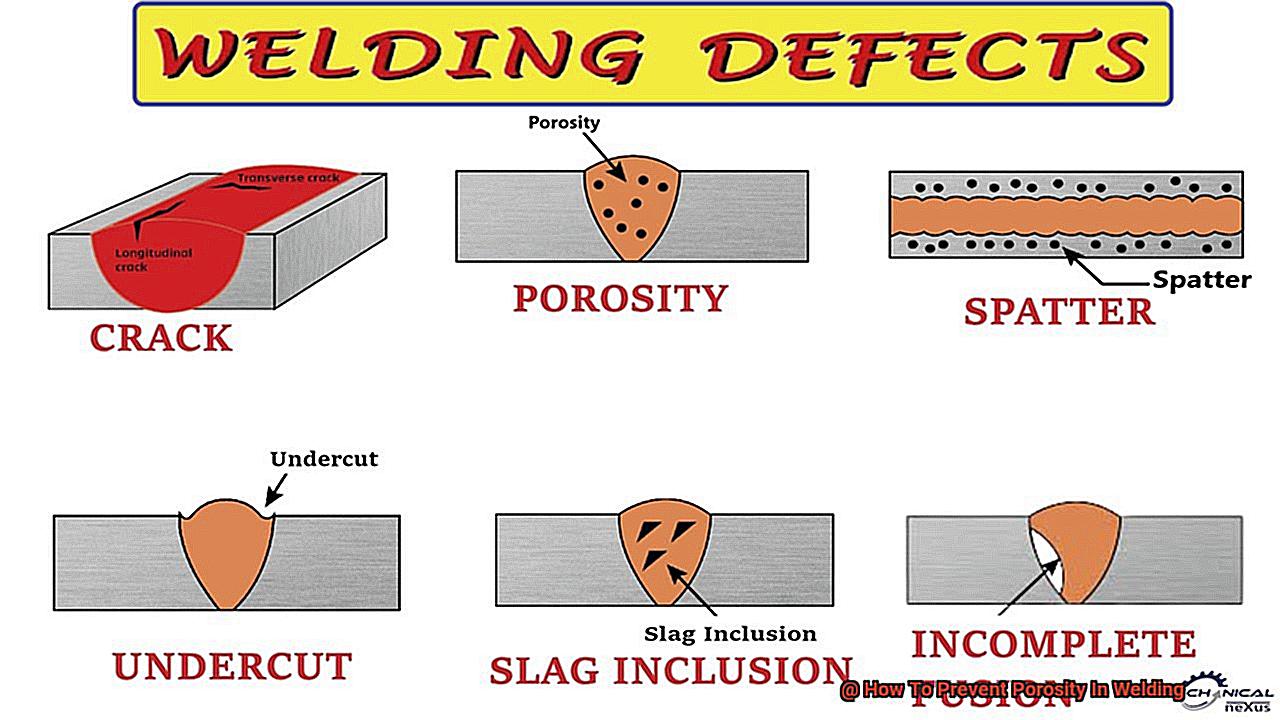
Porosity occurs when gas becomes trapped in the weld pool, creating small voids or holes in the finished product. The causes of porosity can vary, from moisture or contaminants on the surface being welded to incorrect shielding gases and improper welding techniques. To prevent porosity, choosing the right welding technique is crucial.
Gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) and gas metal arc welding (GMAW) are often preferred for their ability to provide better control over the welding process and reduce the risk of porosity. However, some jobs may require other techniques such as flux-cored arc welding (FCAW) or submerged arc welding (SAW), which can also be effective if used correctly.
In addition to selecting the appropriate technique, it’s equally important to choose the right parameters for the job. This includes selecting the correct current, voltage, and wire feed speed for GMAW or the correct amperage and gas flow rate for GTAW. These parameters can vary depending on factors such as the thickness and type of material being welded and the position of the weld.
Moreover, other factors such as proper cleaning and preparation of surfaces, ensuring proper shielding gas flow and coverage, and avoiding excessive movement or manipulation of the weld puddle during the process are all critical in preventing porosity.
By taking these steps and selecting the appropriate technique and parameters for each job, you can significantly reduce the risk of porosity and produce high-quality welds that meet industry standards.
Using Suitable Filler Metals
As a skilled welder, you understand the importance of creating a flawless weld that meets industry standards. One crucial step in achieving this is selecting a suitable filler metal. By using the right filler metal, you can prevent porosity and ensure a strong bond between the base metals.
Choosing the appropriate filler metal depends on various factors, such as the welding process being used and the composition of the base metal. For instance, when using gas tungsten arc welding or TIG welding, it’s best to use filler metals with low hydrogen content to prevent porosity. This is because the heat input is low, and the weld pool is small, making it easier for hydrogen to become trapped in the weld.

In contrast, for gas metal arc welding or MIG welding, you can use filler metals with higher hydrogen content since the heat input is higher, and the weld pool is larger. Additionally, when welding aluminum, it’s crucial to use a filler metal with a similar composition to the base metal to prevent porosity.
Besides choosing the right filler metal, it’s also important to ensure that it’s clean and dry. Moisture or grease on the filler metal can cause gas pockets to form within the weld, leading to porosity. Therefore, it’s essential to store filler metals in a dry and clean environment before use.
To summarize, preventing porosity in welding requires selecting suitable filler metals and ensuring they’re clean and dry. By taking these precautions, you can avoid defects in your welds and ensure a strong and durable bond between the base metals.
RZh8IF6fSic” >
Conclusion
To sum up, porosity in welding poses a significant challenge for welders, as it can weaken the joint and make it less durable. However, by understanding the root causes of porosity and implementing specific strategies to prevent it, welders can produce strong and solid welds without any porosity.
One crucial step in preventing porosity is to prepare the base metal correctly. This involves cleaning it thoroughly using mechanical or chemical methods to ensure that there are no contaminants present. Additionally, choosing the right welding technique and parameters, such as GTAW or GMAW, can help reduce the risk of porosity.
Another essential factor to consider is the filler metal used in welding. Welders should use clean and dry filler metals that are suitable for the job at hand. It’s also critical to maintain proper shielding gas coverage throughout the welding process to prevent air from contaminating the weld pool.
Finally, during the welding process itself, excessive movement or manipulation of the weld puddle should be avoided. By following these practical tips and valuable insights for preventing porosity in welding, both novice and experienced welders can create high-quality welds that meet industry standards.
In conclusion, preventing porosity in welding requires attention to detail and careful consideration of various factors. By addressing these issues head-on, you can produce flawless welded joinings every time.





