Stainless steel is a versatile metal that’s highly valued in various industries, from construction to food processing. Its durability and corrosion resistance make it a popular choice for fabricators and engineers alike. However, welding stainless steel can be a daunting task due to its unique properties.
If you’ve ever attempted to weld stainless steel, you may have wondered if flux core wire is an option. Flux core welding is known for its simplicity and convenience, making it an attractive choice for both professionals and DIY enthusiasts. But is it suitable for welding stainless steel?

In this blog post, we’ll delve into this question in detail and provide you with all the information you need about welding stainless steel with flux core wire. We’ll examine the benefits and limitations of flux core welding, the challenges associated with welding stainless steel, and whether or not this method can be used to join this metal. By the end of this post, you’ll have gained a better understanding of this welding technique and whether it’s suitable for your next project involving stainless steel.
So, let’s dive in.
What is Flux Core Wire Welding?
Contents
- 1 What is Flux Core Wire Welding?
- 2 Why is Flux Core Wire Welding Not Recommended for Stainless Steel?
- 3 What Type of Shielding Gas Should Be Used for Welding Stainless Steel?
- 4 What Are the Challenges of Welding Stainless Steel With Flux Core Wire?
- 5 Safety Protocols to Follow When Welding Stainless Steel
- 6 Conclusion
Among the different types of welding techniques and equipment, Flux Core Wire Welding stands out as a versatile and user-friendly method that produces high-quality welds on thicker metals.
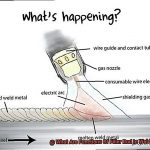
So, what exactly is Flux Core Wire Welding? It’s a welding technique that uses a hollow wire electrode filled with flux. You can think of it as a straw filled with a delicious drink, except that instead of liquid, it’s filled with flux. This flux acts as a protective agent, melting and creating a gas shield around the molten metal, preventing oxidation and other forms of contamination. The process is commonly used in construction, shipbuilding, and other heavy-duty applications.

Flux Core Wire Welding can be performed using either a MIG or MAG welding machine. MIG welding machines use a shielding gas such as argon or helium to protect the weld puddle from contamination. On the other hand, MAG welding machines use a reactive gas such as carbon dioxide or oxygen in addition to the flux core wire to create the protective shield.
However, when it comes to welding stainless steel, Flux Core Wire Welding is not recommended. Stainless steel requires a specific type of shielding gas such as argon or helium to protect the weld from oxidation and other contaminants. Using flux core wire would introduce additional elements into the weld that could potentially compromise its quality and strength.

It’s essential to note that stainless steel has a higher melting point than other metals commonly welded with flux core wire. Therefore, it’s crucial to control the heat generated during the welding process carefully to prevent warping, distortion, or cracking of the stainless steel.

In conclusion, if you’re looking to weld stainless steel, it’s best to consult with a professional who can guide you through the process and ensure that you’re using the proper equipment and technique. Whether you’re a seasoned welder or just starting out, always follow proper safety protocols and take your time to produce the best possible results.
Why is Flux Core Wire Welding Not Recommended for Stainless Steel?
When it comes to welding stainless steel, flux core wire welding is not the way to go. But why, you ask? Well, let’s dive into the reasons why.
Firstly, stainless steel has a low thermal conductivity, which means it requires more heat to weld properly. Unfortunately, flux core wire welding doesn’t provide enough heat to weld stainless steel correctly. It’s like trying to make ice cream with a hairdryer; it just won’t work.
Secondly, the chemical composition of the flux-cored electrode used in flux core wire welding is not suitable for welding stainless steel. The mixture of chemicals released during welding can cause porosity and other defects in the weld. It’s like using gasoline instead of oil in your car; it might seem like a good idea at first, but it will eventually lead to major problems.
Thirdly, stainless steel is more susceptible to heat distortion than other metals. Flux core wire welding produces a lot of heat, which can cause significant warping and distortion, making it challenging to maintain the shape and structural integrity of the welded piece. It’s like trying to straighten out a bent paper clip with a hammer; it’s just not going to work out well.
Finally, flux core wire welding produces a lot of spatter that can be problematic when welding stainless steel. The spatter can cause contamination and lead to lower quality welds. It’s like trying to cook dinner with a dirty pan; you’re not going to get the desired results.
In conclusion, while flux core wire welding may be suitable for other types of metals, it’s not recommended for stainless steel due to its low thermal conductivity, unsuitable chemical composition, susceptibility to heat distortion, and potential for spatter contamination. So next time you’re working with stainless steel, make sure to use the appropriate welding technique to ensure high-quality results.
What Type of Shielding Gas Should Be Used for Welding Stainless Steel?
Welding stainless steel is a tricky business. Just like oil and water, certain combinations don’t mix well. That’s why selecting the right type of shielding gas is crucial for a successful weld.
The most commonly used shielding gases for welding stainless steel are argon and helium, or a combination of both. Argon is an inert gas that provides excellent coverage and protection to the weld pool, preventing oxidation and porosity. It’s like wrapping your weld in a cozy blanket, keeping it safe from harm.
However, if you want to take your welding game to the next level, helium is your go-to gas. Helium has a higher thermal conductivity than argon, which can improve penetration and reduce heat input. It’s like having a superpower that can cut through metal with ease.
But wait, there’s more. Why settle for one when you can have both? A mixture of argon and helium can provide the benefits of both gases, such as better arc stability, deeper penetration, and a faster welding speed. It’s like having a dynamic duo that complements each other’s strengths.
But what about flux core wire? This type of wire eliminates the need for shielding gas altogether by having a flux coating that releases a shielding gas as it melts, protecting the weld from oxidation and contamination. However, keep in mind that flux core wire has its limitations and may not be suitable for all stainless steel welding applications.
In summary, selecting the right type of shielding gas for welding stainless steel depends on the specific application and desired outcome. To find that perfect balance for a successful weld, consult with a welding expert or refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations before selecting a shielding gas.
What Are the Challenges of Welding Stainless Steel With Flux Core Wire?
Welders must overcome several obstacles to create a strong and durable weld.
The first challenge is the high level of oxidation resistance present in stainless steel. This resistance makes it difficult for the flux core wire to penetrate the metal and create a weld that is strong enough to withstand pressure and stress. It’s like trying to cut through a thick steak with a dull knife – you need more effort and precision.
Another challenge is porosity, which weakens the strength and durability of the weld. When welding stainless steel with flux core wire, excess gas can be produced during the welding process due to the wire’s high carbon content, causing gas pockets to become trapped in the weld. It’s like trying to bake a cake that ends up with air pockets inside – it won’t hold up well.
Stainless steel’s high thermal conductivity can also pose challenges during welding. The metal quickly dissipates heat away from the weld pool, making it challenging for welders to maintain proper temperature and prevent cracks or other defects from forming in the weld. It’s like cooking a delicate dish on a stove that heats up too quickly – you need to be cautious not to burn it.
Lastly, selecting the right flux core wire for welding stainless steel can be daunting. Different types of flux core wires have different properties and are designed for use with specific types of metal. Welders must select a flux core wire that is specifically designed for stainless steel to achieve optimal results.
Despite these challenges, welders can overcome them by understanding how each obstacle affects the welding process and taking necessary precautions. By doing so, they can create a strong and durable weld on their stainless steel projects.
In conclusion, welding stainless steel with flux core wire is not impossible, but it does come with its challenges. Welders must be aware of oxidation resistance, porosity, thermal conductivity, and selecting the right flux core wire.
Safety Protocols to Follow When Welding Stainless Steel
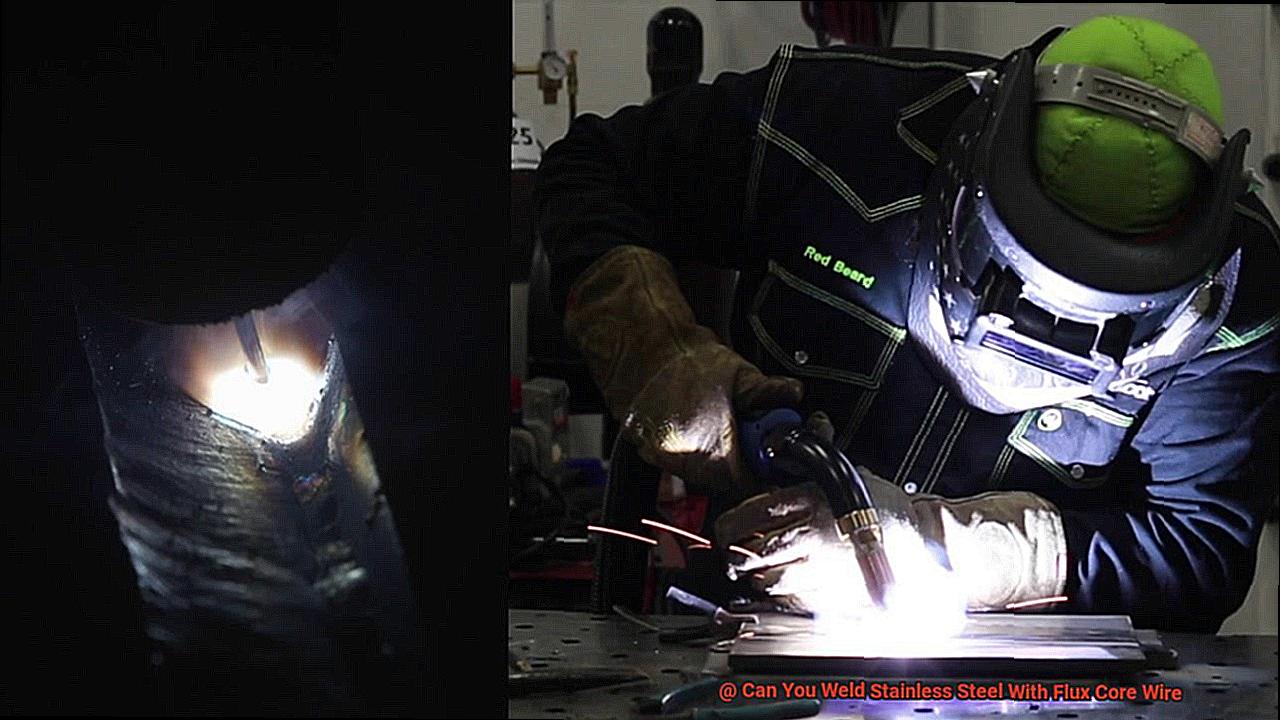

Welding stainless steel with flux core wire is like a graceful dance, but one must always be mindful of the potentially harmful fumes that can arise. Following proper safety protocols is essential to ensure a safe and successful outcome.
First and foremost, it’s crucial to work in a well-ventilated area. Imagine taking in a breath of fresh air after being cooped up inside all day. Working in an open-air space or a room with adequate air circulation can prevent exposure to dangerous fumes such as hexavalent chromium, which is a known carcinogen. If working indoors, use a ventilation system that effectively captures and removes the fumes from the environment.
Next, it’s time to gear up with the proper personal protective equipment (PPE). Wearing a welding mask or helmet with eye protection, gloves, and protective clothing such as a welding jacket or apron is critical when welding stainless steel with flux core wire. Think of it like donning armor before going into battle- PPE shields you from potential harm.
Lastly, it’s essential to avoid touching any hot surfaces or materials during and immediately after welding. Stainless steel can reach high temperatures during the welding process, and contact can result in severe burns or other injuries. It’s like steering clear of the stove burners after cooking up a delicious meal- you don’t want to get burned.
d-PDy1Uzypk” >
Conclusion
To sum it up, using flux core wire to weld stainless steel is not recommended. This is because of its low thermal conductivity, unsuitable chemical composition, susceptibility to heat distortion, and potential for spatter contamination. While flux core wire welding may work well with other metals, it’s crucial to use the appropriate welding technique when working with stainless steel to ensure high-quality results.
When welding stainless steel, selecting the right shielding gas is critical for a successful weld. Argon and helium are commonly used shielding gases for welding stainless steel or a combination of both. However, keep in mind that flux core wire has limitations and may not be suitable for all stainless steel welding applications.
Welders must overcome several challenges when working with stainless steel using flux core wire. These obstacles include oxidation resistance, porosity, thermal conductivity, and selecting the right flux core wire. To create a strong and durable weld on their stainless steel projects, welders must understand how each obstacle affects the welding process and take necessary precautions.
Lastly, safety protocols are non-negotiable when welding stainless steel with flux core wire. It’s essential to protect oneself and others from potential harm or injury by consulting with a professional and taking proper safety measures.