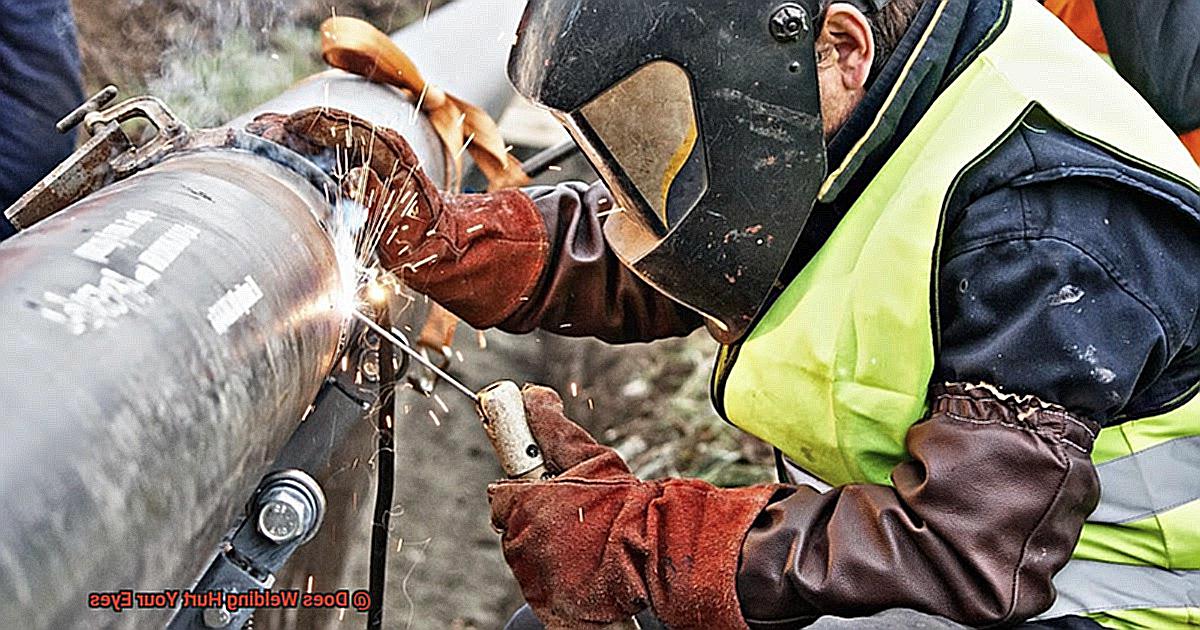
Welding, a process used in various industries from construction to manufacturing, emits a bright glare and flashes that are hard to ignore.
As a seasoned welder or newbie, you might wonder if welding hurts your eyes. The answer is yes – if you don’t take necessary safety precautions.
The ultraviolet rays and intense light emitted during welding can cause temporary and permanent damage to your eyes if left unprotected. Photokeratitis, a condition similar to sunburn, can occur due to exposure to UV rays.
Moreover, the retina can burn from intense light, causing permanent eye damage. To protect your eyes as a welder, it’s crucial to take the necessary precautions.
Welding helmets or face shields with auto-darkening lenses are designed explicitly to safeguard your eyes from harmful UV rays and sparks generated during welding. They also protect against intense heat during welding.
In summary, failing to take the necessary safety measures while welding could result in temporary or permanent eye damage and future loss of work in the industry. It’s essential always to wear protective gear such as helmets and other protective clothing while welding.
Protecting your eyes is vital for maintaining good vision throughout your career as a welder.
a. Definition of Welding
Contents
Welding is an essential process used in many industries, from constructing buildings and bridges to repairing machinery and vehicles.
It involves joining two or more metal pieces together by heating them to their melting points and then allowing them to cool and fuse together. However, welding can be a dangerous job if safety measures are not taken seriously.
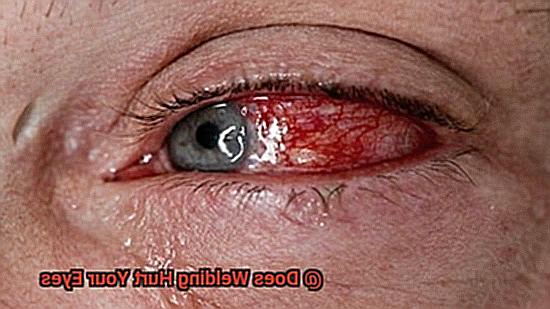
One of the most significant hazards of welding is the exposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation. The bright light produced by the welding arc can cause severe damage to the eyes, leading to painful conditions such as welder’s flash, also known as arc eye.
The symptoms of welder’s flash include redness, tearing, and sensitivity to light, which can cause extreme discomfort and hinder a welder’s ability to work. To prevent such hazards, welders must always wear appropriate eye protection at all times.
This includes a welding helmet with a shaded lens that blocks UV radiation and glare from the welding arc. Additionally, safety glasses should be worn underneath their helmets to provide additional protection from flying debris and sparks.
It’s important to note that eye damage caused by welding can lead to severe eye problems such as photokeratitis, cataracts, and retinal damage. Photokeratitis is a painful condition caused by inflammation of the cornea due to overexposure to UV radiation.
Cataracts are a clouding of the lens in the eye caused by prolonged exposure to UV radiation and can lead to vision loss if left untreated. Retinal damage is caused by exposure to both UV radiation and visible light and can lead to a loss of central vision.

Wearing appropriate protective gear such as welding helmets with shaded lenses and safety glasses or goggles is crucial in filtering out harmful radiations that cause eye damage.
b. Overview of Eye Hazards Associated with Welding
Welding is a fascinating and lucrative profession that creates strong metal structures, but it also poses significant risks to the welder’s eyesight.
The welding process can release harmful ultraviolet (UV) and infrared (IR) radiation, as well as flying debris, that can lead to a range of painful and serious eye conditions. One of the most common eye hazards associated with welding is “welder’s flash” or photokeratitis, which can cause redness, irritation, and extreme sensitivity to light.
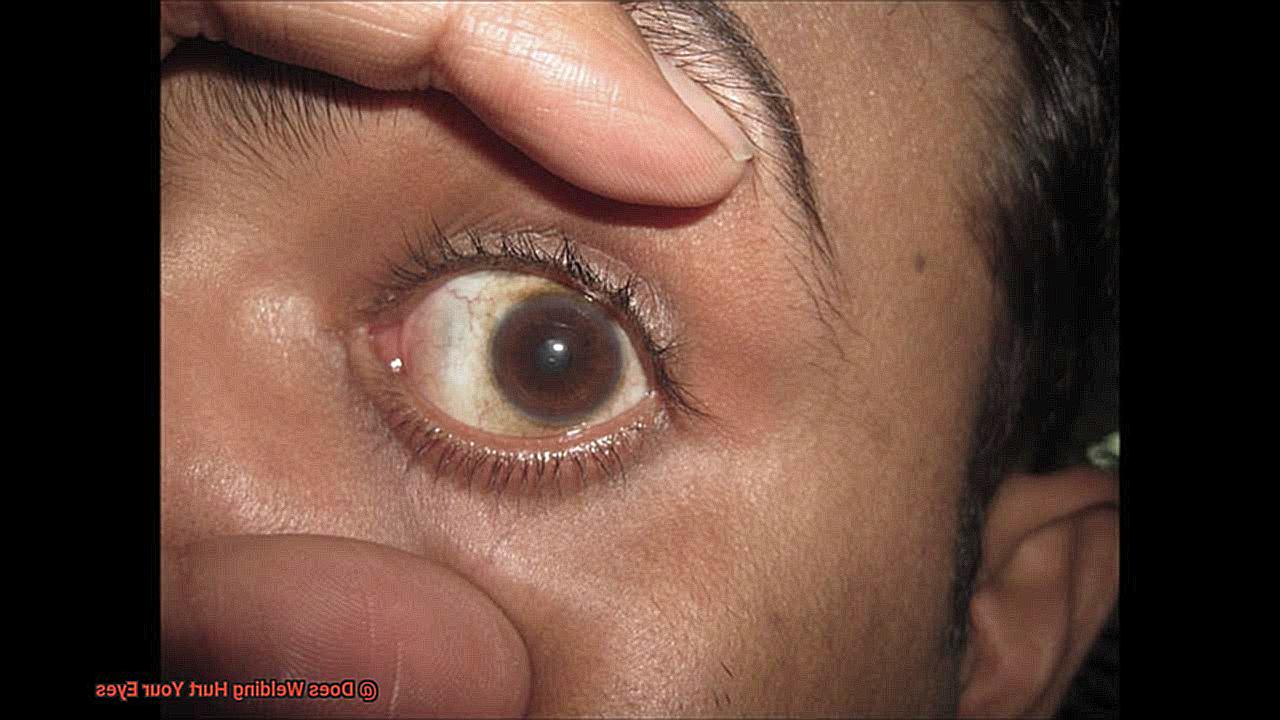
Welders are also at risk of developing cataracts and pterygium, which are caused by long-term exposure to UV radiation and IR radiation, respectively. These conditions can lead to permanent vision loss if left untreated.
Flying debris or particles from the welding process can also cause painful corneal abrasions that can lead to vision problems. To protect against these hazards, welders must wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including safety glasses or goggles with side shields and a welding helmet with a filter lens to protect against UV and IR radiation.
Regular eye exams are essential for welders to detect any potential eye problems early on. Prompt medical attention is necessary if an injury or vision problem occurs to prevent further damage.
Prevention is key when it comes to protecting eyesight. In conclusion, while welding is a rewarding profession, it poses significant risks to welder’s eyesight.

By wearing proper PPE and seeking regular eye exams, welders can protect their eyesight and continue their career in welding safely.
What is UV Radiation?
UV radiation is a type of electromagnetic radiation that is present in sunlight and some artificial sources, including welding arcs.
It’s classified into three types; UVA, UVB, and UVC. UVA is the most common type of UV radiation that can penetrate the skin and cause aging and wrinkles.
UVB is responsible for sunburns and skin cancer, while UVC is the most hazardous type of UV radiation but mostly absorbed by the ozone layer. However, when welding, the UV radiation produced is mostly UVC, which is not present in sunlight.
Hence, welders are at a higher risk of being exposed to harmful UV radiation than the general public. Welding arcs produce intense light that can cause flash burns, which are painful injuries to the eyes that can result in temporary or permanent vision loss.
The intensity of the UV radiation produced during welding depends on several factors, including the welding technique used, the type of metal being welded, the distance between the welder and the arc, and the duration of exposure. To prevent eye damage from welding, it’s crucial for welders to wear appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
Safety glasses or goggles with side shields and a face shield with a filter lens should be worn to provide adequate protection against harmful UV radiation. Welders should also ensure they have proper ventilation in their workspace and take regular breaks to reduce their exposure to harmful UV radiation.
Welders who do not take proper precautions to protect their eyes from UV radiation can develop a condition called welder’s flash or arc eye. The symptoms of this condition include redness, sensitivity to light, tearing, and a feeling of grittiness in the eyes.
Hence, protecting your eyes with the appropriate PPE, seeking regular eye exams, and prompt medical attention are crucial to preventing permanent vision loss caused by harmful radiation and flying debris.
How Does UV Radiation Damage the Eyes?
This type of energy, which comes from the sun and welding arcs, can cause severe damage to our eyes if we’re exposed to it for extended periods of time.
Cataracts are one of the most common eye problems caused by UV radiation. It occurs when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy or opaque, leading to blurry vision and difficulty seeing clearly.
Another condition that can be caused by exposure to UV radiation is pterygium. This is a growth of tissue on the white part of the eye that can cause redness, irritation, and discomfort.
Photokeratitis is yet another painful condition that can occur due to overexposure to UV radiation. This is commonly referred to as “welder’s flash” and can lead to symptoms like pain, redness, tearing, and sensitivity to light.
So how exactly does UV radiation cause these problems? Essentially, it breaks down the cells in the lens and cornea over time.
This damage accumulates and can eventually lead to severe eye problems like cataracts and pterygium. In addition, UV radiation can cause inflammation and irritation of the eyes which can result in discomfort and pain.
It’s crucial for welders to protect their eyes from UV radiation by using proper safety gear while working. This includes wearing welding helmets with shaded lenses that block out harmful UV radiation.
Additionally, taking frequent breaks to rest their eyes and avoiding prolonged exposure to welding arcs can significantly reduce their risk of developing eye problems. In conclusion, it’s important to remember that UV radiation poses a significant threat to our eyes if left unprotected.
Cataracts, pterygium, and photokeratitis are just a few examples of the serious eye conditions that can be caused by overexposure to UV radiation.
Photokeratitis (Welder’s Flash)
As a skilled welder, you know that protecting your eyes is crucial.
They are not only essential for your work but also for your quality of life outside of work. However, welders face a significant risk of developing photokeratitis, also known as “Welder’s Flash,” which can cause excruciating pain and temporary vision loss if left untreated.
Fortunately, there are steps you can take to safeguard your eyes from this painful condition. Photokeratitis occurs when the cornea is exposed to intense ultraviolet (UV) light.
Welding arcs emit high levels of UV radiation, causing inflammation, swelling, and redness in the eyes. Symptoms include pain, tearing, and sensitivity to light.
The best way to prevent photokeratitis is by wearing appropriate eye protection. Invest in a high-quality welding helmet or goggles with specialized lenses designed to block UV light.
These lenses come in either tinted or clear options based on the type of welding you do. It is vital to take regular breaks during your welding sessions and avoid staring directly at the welding arc for extended periods of time.
Implementing these simple steps can help reduce your risk of developing photokeratitis and other eye injuries. If you suspect that you may have photokeratitis, seek medical attention immediately.
Your doctor can provide treatment to manage your symptoms and prevent any long-term damage to your eyesight.
Cataracts
As a welder, your eyes are your most precious asset.

However, one of the most severe eye conditions that can result from welding is cataracts. Cataracts occur when the lens in your eye becomes clouded, causing vision loss and even blindness.

Welding poses a significant risk of developing cataracts due to exposure to high levels of ultraviolet (UV) radiation. Several factors determine the risk of developing cataracts from welding, including the duration and intensity of exposure, the type of welding performed, and protective eyewear used.
Shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) or gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) pose a higher risk than other types of welding. Symptoms of cataracts include blurry vision, difficulty seeing at night, sensitivity to light, and faded colors.
If left untreated, cataracts can lead to permanent vision loss. However, with cataract surgery, it is possible to remove the damaged lens and replace it with an artificial one, restoring your vision.
To prevent cataracts from developing due to welding, it is vital to wear proper eye protection. Safety glasses or goggles with side shields that block out UV radiation should be worn while welding.
A welding helmet with a filter shade that provides adequate protection for the specific type of welding being performed is also necessary. Taking regular breaks to give your eyes a rest and avoid prolonged exposure to UV radiation can further reduce the risk of developing cataracts.
By wearing proper eye protection and taking regular breaks, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing this condition and maintain good vision for years to come.
Retinal Damage
The retina is a critical component of the eye that receives light and sends visual signals to the brain. When exposed to UV radiation and intense visible light during welding, the retina can become damaged.
There are two types of retinal damage that can occur: photokeratitis and retinal burn. Photokeratitis, also known as “welder’s flash,” is a painful condition that occurs when the cornea becomes inflamed due to exposure to UV radiation.
Symptoms include redness, tearing, and sensitivity to light. Fortunately, this condition usually lasts for a few days before resolving on its own.
Retinal burn, on the other hand, is a much more severe condition that can cause permanent damage to the retina. It occurs when intense light emitted during welding causes thermal damage to the retina.
The symptoms of retinal burn may not be immediately apparent and can take several hours or even days to develop. These symptoms include blurred vision, blind spots, or even complete vision loss.
To prevent retinal damage, it is crucial for welders to take appropriate precautions such as wearing personal protective equipment (PPE). By wearing welding helmets with proper shade lenses and safety glasses with side shields, welders can reduce their exposure to UV radiation and intense light emissions during welding.
These measures can help prevent both photokeratitis and retinal burn. In conclusion, it is essential for welders to prioritize eye protection while on the job.
Wearing appropriate PPE such as welding helmets and safety glasses with side shields is critical in preventing serious retinal damage that could result in permanent vision loss.
0AueSEjshUw” >
Protective Gear for Welders
The intense light and heat produced during welding can cause serious damage to your eyesight, such as arc eye, which is essentially a sunburn on the surface of the eye.
Therefore, it is not just an option but a necessity to wear protective gear. The most common type of protective gear for welders is the welding helmet.
This helmet is specifically designed to protect your entire face and head from radiation, flying debris, and sparks. It also comes with a flip-up lens that allows you to see what you are working on without needing to remove the helmet.
However, having a welding helmet alone may not offer complete protection. It is crucial to wear safety glasses or goggles underneath the helmet for added protection.
These glasses should be made from impact-resistant materials and have side shields to prevent any particles from entering the eyes from the sides. Different types of welding require varying levels of protection; therefore, it is essential to consult with your supervisor or safety manager to determine the appropriate level of protection for your specific job.
For instance, TIG welding produces less radiation than MIG welding, so the required level of protection may be lower. In conclusion, wearing proper protective gear is crucial for welders to avoid any harm or injury while performing their tasks.
Also Read: What does welding flash feel like? – The Welding Guru
Conclusion
In conclusion, welding is a high-risk job that can take a toll on your eyesight if you’re not careful.
The intense light and radiation emitted during welding can cause severe eye damage, including photokeratitis, cataracts, pterygium, and retinal damage. But don’t worry; you can protect yourself by wearing the right personal protective equipment (PPE).
Welders must wear welding helmets with shaded lenses and safety glasses or goggles with side shields to shield their eyes from harmful UV radiation and flying debris. It’s also crucial to take regular breaks during welding sessions and avoid staring directly at the welding arc for extended periods.
Remember that prevention is always better than cure. By taking appropriate precautions and seeking prompt medical attention if you experience any symptoms of eye damage, you can reduce your risk of developing serious eye problems that could result in permanent vision loss.





