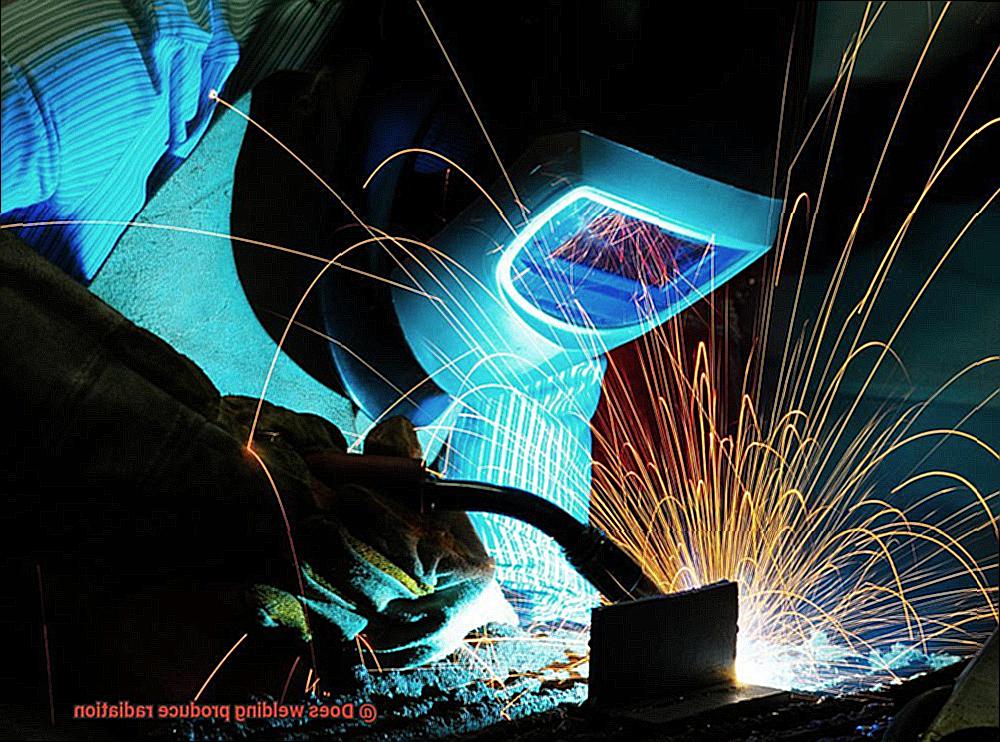
Welding is an essential process in various industries, such as construction, machinery, and manufacturing.
It involves melting two metal pieces together using high heat. However, welding also releases intense light, heat, and fumes that pose risks to welders and those nearby.
One of the primary concerns about welding is radiation exposure. Radiation is a type of heat that travels through materials and space.
Welding produces different forms of radiation, including ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) light. UV radiation can cause skin burns, eye damage, and increase the risk of skin cancer.
On the other hand, IR radiation can cause thermal damage to the skin and eyes if welders don’t wear appropriate PPE. In this essay, we’ll delve into the subject of “Does welding produce radiation?”
Let’s get started now.
What Types of Radiation Does Welding Produce?
Contents
- 1 What Types of Radiation Does Welding Produce?
- 2 Are There Health Risks Associated with Welding Radiation?
- 3 How Can Welder’s Protect Themselves from Radiation Exposure?
- 4 What is Ionizing Radiation and How Does it Differ from Non-Ionizing Radiation?
- 5 What are the Dangers of Ultraviolet (UV) Light Exposure in Welders?
- 6 Are There Regulations for Controlling Welders’ Exposure to Radiation?
- 7 Conclusion
Welding is a crucial process in many industries, but it’s essential to note that it produces several types of radiation that can be harmful to human health.
Let’s dive into the three primary forms of radiation created during welding and the potential health risks associated with each. Firstly, ultraviolet (UV) radiation is generated during welding, and it’s the most common form of radiation produced.
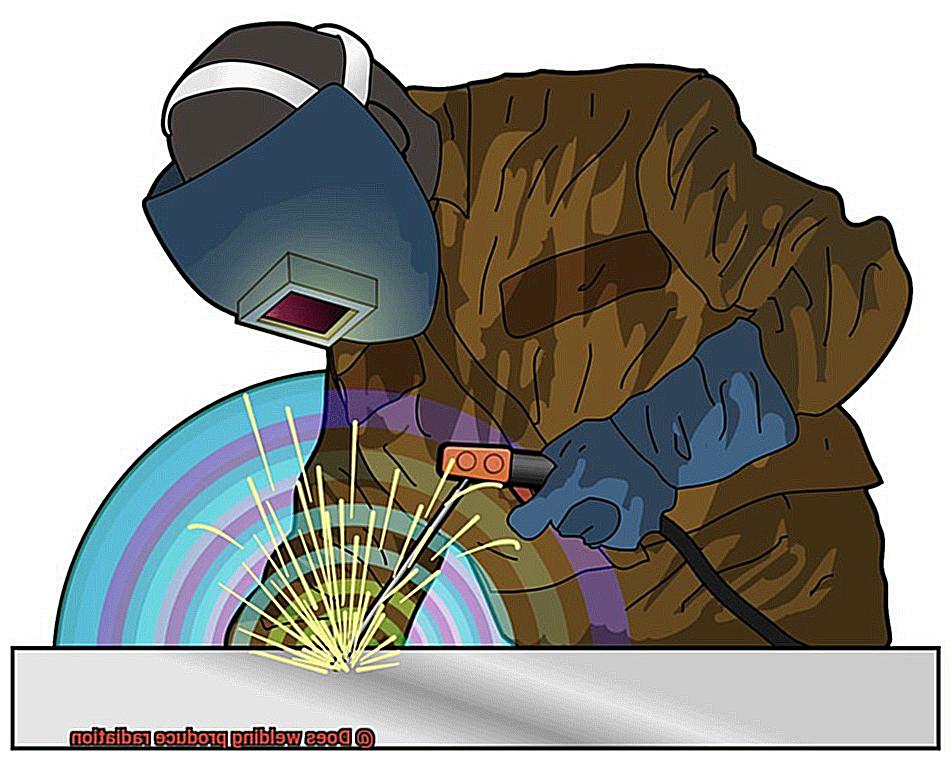

This type of radiation is invisible to the naked eye and can cause severe skin and eye damage if employees are not adequately protected. The amount of UV radiation produced during welding depends on numerous factors, such as the type of welding process, welding current, voltage, and speed.
Welders who work outdoors or in areas with inadequate ventilation are at a higher risk of UV radiation exposure. Secondly, visible light radiation is another form of radiation produced during welding.
This type of radiation is visible to the naked eye and can result in temporary blindness if workers look directly at the welding arc without proper protection. The intensity of visible light produced during welding varies depending on the type of welding process and the amount of current used.
Thirdly, infrared radiation is generated during welding, which produces heat and melts the metal being welded. It can also cause skin burns and eye damage if workers aren’t adequately protected.
It’s worth noting that welding doesn’t produce ionizing radiation that can cause cancer or genetic damage. However, prolonged exposure to UV and visible light radiation produced during welding can increase the risk of developing skin cancer, cataracts, and other eye diseases.

To minimize potential health risks involved with welding, it’s crucial to take appropriate safety precautions when working. Welders should wear protective clothing, use proper ventilation, and avoid looking directly at the welding arc without having proper protection.
It’s also important to choose the right welding process for the job and follow best practices to minimize exposure to harmful gases in welding fumes. In conclusion, while welding is a vital process in many industries, it’s crucial to understand the types of radiation produced during welding and their potential health risks.

Taking proper safety precautions can minimize exposure and reduce short-term and long-term health risks associated with welding.
Are There Health Risks Associated with Welding Radiation?
Welding is more than just a craft; it’s a process that requires precision, accuracy, and a steady hand.
However, did you know that welding can pose significant health risks to employees if they aren’t properly covered? In this blog post, we’ll discuss the health risks of welding radiation and what welders and their employers can do to minimize them.
The high temperatures produced during welding can release harmful radiation, including ultraviolet (UV) radiation, visible light radiation, and infrared radiation. Long-term exposure to UV radiation is the most significant health risk associated with welding radiation, as it can lead to skin cancer, cataracts, and other eye diseases.
The amount of UV radiation emitted during welding depends on the type of welding process used, the type of metal being welded, and the intensity and duration of the welding arc. However, that’s not all: Welders are also vulnerable to inhaling harmful fumes during the welding process.
These fumes are a mixture of tiny metal particles that can cause respiratory difficulties such as bronchitis, asthma, and pneumonia. Long-term exposure to these fumes has been linked to an elevated risk of lung cancer.
Certain welding techniques, such as gas tungsten arc welding (GTAW) and plasma arc welding (PAW), expose workers to ionizing radiation. This kind of radiation has enough energy to separate electrons from atoms or molecules in the body, leading to an increased risk of cancer over time.
So what can welders and their employers do to eliminate these risks? First and foremost, welders must use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE), including gloves, safety glasses or goggles, respirators, and welding helmets with appropriate filters to block UV radiation.
Employers must also provide ventilation systems and ensure that all welding equipment is correctly maintained to minimize the release of fumes into the air. In conclusion, while welding is an essential process in many industries, it’s crucial for welders and their employers to take necessary precautions to protect themselves from harmful radiation exposure.
By wearing appropriate PPE and ensuring that proper ventilation systems are in place, welders can minimize their risk of developing serious health problems associated with welding radiation exposure.
How Can Welder’s Protect Themselves from Radiation Exposure?
Welding involves high heat and produces various types of radiation, including ultraviolet, visible light, and infrared radiation.
To minimize the risks associated with radiation exposure, welders must take appropriate measures to protect themselves. Personal protective equipment (PPE) is one of the most effective ways to shield against radiation contamination.
Welders should wear protective clothing made of flame-resistant materials, such as long-sleeved shirts, pants, and gloves. Furthermore, welding helmets with filter lenses that block harmful radiation from entering the atmosphere are a must-have for welders.
Proper ventilation in the welding area is also crucial to mitigate radiation exposure risks.
When inhaled, welding produces fumes and gases that can be harmful. Welders should work in well-ventilated areas or use local exhaust ventilation systems that remove smoke and gases from the welding area.
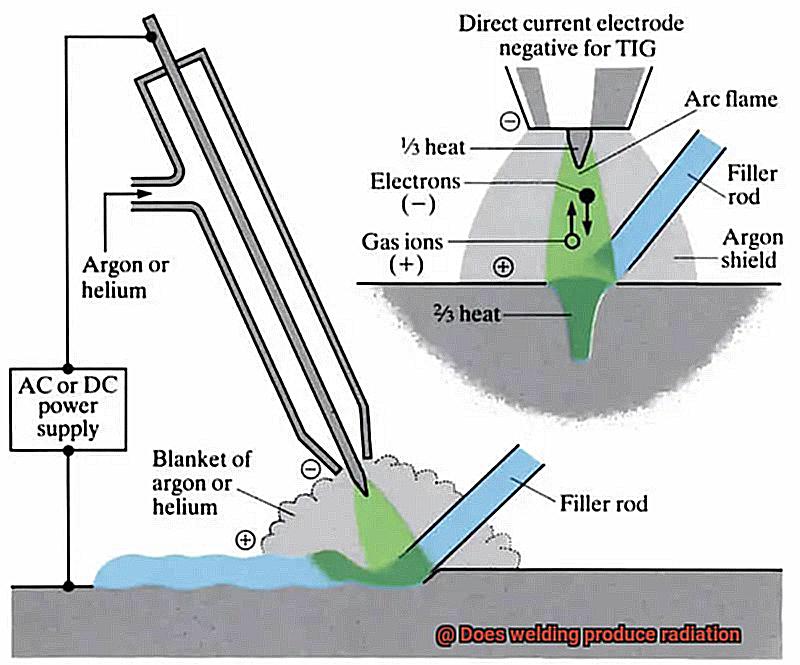
In addition to using PPE and ensuring proper ventilation, welders must be educated on safe welding techniques and recognize the dangers associated with radiation exposure.
They should be aware of the symptoms of radiation sickness, which include skin irritation, eye irritation, and fatigue. Knowledge is power – knowing the risks will help you take the right precautions.

Lastly, routine medical check-ups are essential for welders to monitor their health and detect any health problems early on. Regular medical examinations can help identify and treat health issues before they become chronic.
So, welding involves significant health risks due to radiation exposure.
However, welders can minimize their exposure to harmful radiation and protect their health by using personal protective equipment, working in well-ventilated areas, understanding the risks of radiation exposure, and undergoing regular medical check-ups.
What is Ionizing Radiation and How Does it Differ from Non-Ionizing Radiation?
Radiation can be classified into two categories: ionizing and non-ionizing.
Ionizing radiation is like a superhero with incredible energy that can remove tightly bound electrons from atoms, creating ions. It is hazardous to living tissue as it has enough energy to break chemical bonds within cells, potentially leading to DNA damage and health issues such as cancer.
X-rays and gamma rays are examples of ionizing radiation. On the other hand, non-ionizing radiation does not have enough energy to remove electrons from atoms and create ions.
While it is generally safe at low levels, it can cause thermal effects, such as heating of tissues, at higher levels. Radio waves, microwaves, and visible light are examples of non-ionizing radiation.
When it comes to welding, the primary concern is ionizing radiation. Welding produces various types of ionizing radiation, including alpha particles, beta particles, neutrons, X-rays, and gamma rays.
The amount and type of radiation produced depend on several factors like the welding process used and the materials being welded. To safeguard yourself from harmful ionizing radiation exposure while welding, you must take appropriate safety measures.
This includes wearing protective clothing and gloves and monitoring radiation levels in your workspace. In conclusion, it is crucial for welders to know the differences between ionizing and non-ionizing radiation to ensure their safety when working with volatile materials.
What are the Dangers of Ultraviolet (UV) Light Exposure in Welders?
The welding arc emits UV radiation, which can lead to severe skin and eye damage, including sunburn, cataracts, and even blindness.
But there’s no need to worry. By taking a few simple steps, you can protect yourself and avoid long-term health problems.
It’s important to note that the intensity of UV radiation varies depending on several factors, such as the type of welding process, the materials being welded, and your distance from the arc. While tungsten inert gas (TIG) welding generates less UV radiation than other methods like shielded metal arc welding (SMAW) or gas metal arc welding (GMAW), it’s still crucial to take precautions.
One effective way to protect yourself from UV radiation is by wearing protective clothing and accessories. Long-sleeved shirts, pants, gloves, and helmets with a shaded lens are all great options.
Additionally, using a welding curtain or screen can help prevent bystanders from being exposed to harmful UV light. However, protection against UV radiation isn’t only limited to preventing sunburns and eye damage.
Long-term exposure to high levels of UV radiation increases the risk of developing skin cancer, making it crucial to take preventive measures such as using sunscreen with a high SPF rating and getting regular skin checkups. In summary, welders face significant risks from UV radiation exposure.
It’s vital to take preventive measures like wearing protective gear, using a welding curtain or screen, and taking steps against long-term exposure.
Are There Regulations for Controlling Welders’ Exposure to Radiation?
Welding is a craft that requires skill, precision, and an understanding of the potential risks involved.
One such risk is exposure to harmful levels of radiation, which can cause serious health problems if left unaddressed. Luckily, there are regulations in place to protect welders from these risks.
The Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA) has established permissible exposure limits (PELs) for radiation exposure in the workplace, including welding. These limits are specifically designed to protect workers from the adverse effects of radiation, such as skin cancer, cataracts, or even blindness.
Employers have a responsibility to provide proper training and equipment to ensure welders are shielded from radiation exposure in accordance with these laws. Personal protective equipment such as welding shields or helmets with filters that block out harmful levels of radiation are essential.
Additionally, employers must regularly monitor the workplace to ensure radiation levels remain safe. It’s crucial for welders to take responsibility for their own health by following all safety protocols and wearing appropriate protective gear at all times while welding.
Exposure to radiation can be detrimental to your health, so prevention is key. In conclusion, there are regulations in place to safeguard welders from radiation exposure.
O5dQF5uWNhU” >
Conclusion
Welding is a crucial process in various industries, but it comes with some serious hazards to welders and those nearby.
One of the most frequently asked questions about welding is whether it produces radiation. The answer is yes, it does produce radiation, but not all types are harmful.
During welding, ultraviolet (UV), visible, and infrared (IR) light are emitted. UV radiation can cause skin burns, eye injuries, and increase the risk of skin cancer.
Without proper personal protective equipment (PPE), IR radiation may cause thermal damage to the skin and eyes. Although welding does not produce ionizing radiation that causes cancer or genetic damage, prolonged exposure to UV and visible light radiation can increase the risk of developing skin cancer, cataracts, or other eye diseases.
Therefore, taking appropriate safety precautions while working is critical. Employers must install ventilation systems to minimize fumes released into the air and ensure that all welding equipment is correctly maintained.
By knowing the types of radiation produced during welding and their potential health risks while taking necessary safety measures to minimize exposure welders can protect their long-term health and prevent future health issues.





